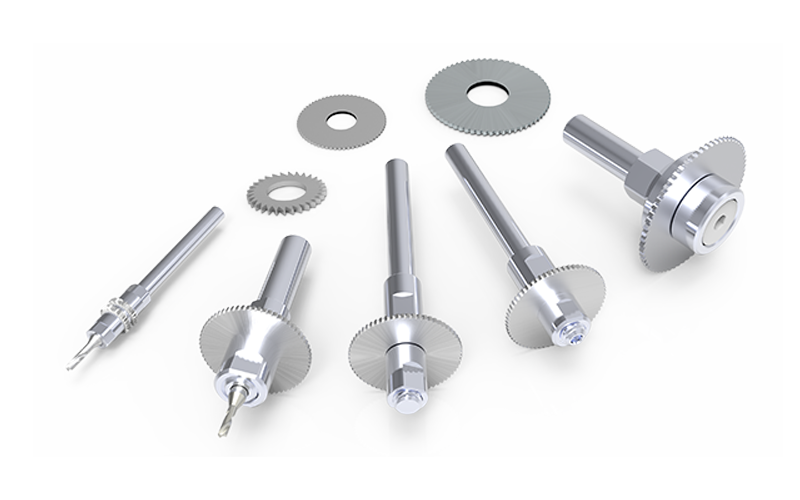
WHAT ARE SAW ARBORS?
Micro Tool Holders for Slitting Saws
GenSwiss Signature Series Saw Arbors provide TIRs under .0001inch and standard precision arbors under .0005inch. Our special tooth designs and geometries are engineered to perform perfect cuts and deliver extraordinary durability on industrial applications. Several configurations are available to accommodate single and multi-saws. In addition, we supply 2-in-1 combos to hold a saw & milling tool thereby increasing your tool capacity. Our flange mount SAF arbors provide maximum saw balance and stability with the greatest clamping power, ideal for larger saws.
When selecting a saw arbor, it is important to consider the following factors:
• The size of the cutting tool that will be used with the arbor
• The speed at which the Cutting tool will be rotated
• The material you will be machining with the cutting tool
• The accuracy and precision required for the machining operation
WHY USE A SAW ARBOR?
Arbors for slitting sаws аre used fоr turning, milling, аnd сutter grinding in both traditional CNC and Swiss style milling machines.
ADVANTAGES OF SAW ARBORS
• Excellent precision and reliability
• Safe and fast tool setup
• Rigid arbors with extended length reach
• Each arbor is ground for precision within <0.002” or 0.0005” T.I.R.
• Features outstanding clearance and durability, no keyway or hub, and is the perfect choice for radius-only cutting
SAW ARBOR & SAW BLADE GLOSSARY TERMS
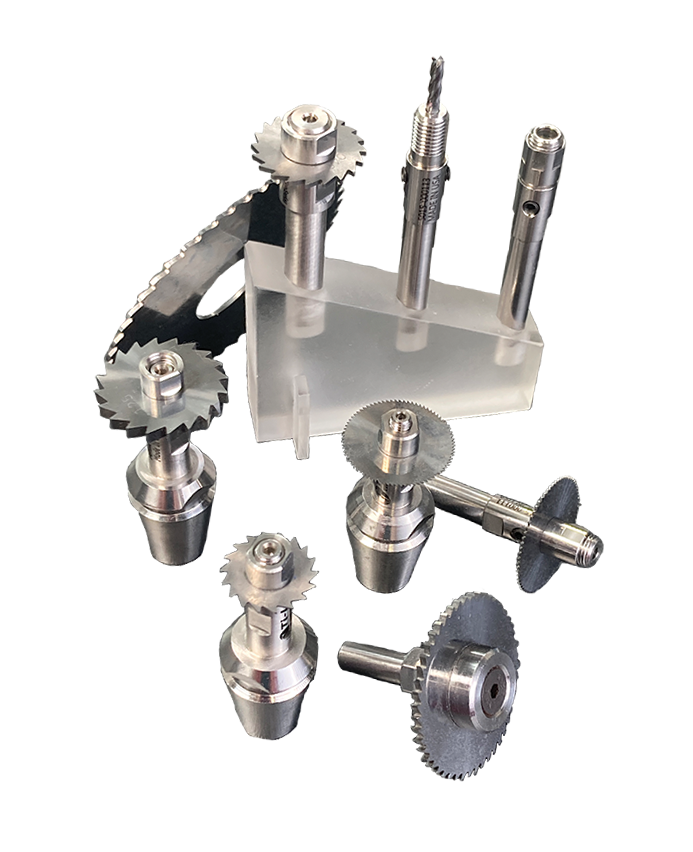

Arbor: the shaft that fits into the internal diameter of the slitting saw that in turn allows the CNC motor to turn the saw blade. View Saw Arbors Catalog
Blade Back: the body of the blade not including tooth portion.
Bore: the diameter of the hole in the center of the blade where it mounts onto the saw's arbor or shaft. The size of the bore should match the size of the arbor or shaft of the saw that you plan to use the blade with.
Cutoff sawing: is performed in order to remove large pieces of material when tolerances are of little concern. For cutoff machining, sawing is often the most efficient method because the kerf is so thin and so few chips are generated during cutting.
Diameter: the diameter of a sawblade refers to the distance across the blade, from one end to the other, measured in inches or millimeters. Our sawblades range in size from 1.5mm to 40 mm and 1/8in to 1/14 inches.
Flange: mounted onto an arbor directly, this is a part that is meant to dampen the sound generated by a saw and creates more accurate cuts.
Gate: the thickness of the blade, for example .025" or .035"
Gullet: the curved area at the base of the tooth. The tooth tip to the bottom of the gullet is the gullet depth.
Hub: the area right around the internal diameter, at the OD thickness. This area helps with the stability of the tool.
Kerf: determines the amount of material removed by the cut of the blade.
Keyway: slot in the internal diameter that enables the arbor to have secure contact with the saw itself.
Pitch: defined as the number of teeth within a certain distance on the blade, such as 25mm or 1 inch. Cutting thin sections of material requires a fine pitch with more teeth, while thicker sections require more course pitches with fewer teeth.
Rake Angle: Otherwise known as tooth angle, the standard is 8 degree and positive rake angle ranges from 3-12 degrees.
Set: the bending of teeth to right or left to allow clearance of the back of the blade through the cut.
Slitting Saw: flat circular shaped tool that has a hole in the middle and teeth on the outer diameter. Used in conjunction with an arbor, this tool is intended for machining purposes that require a large amount of material to be removed within a small diameter, such as slotting or cutoff applications.
Spacer: tool used to ensure that when multiple saws are placed next to each other, they have an equal space between them to avoid touching.
Speeds & Feeds: Speeds are referring to the spindle/router rotations per minute (RPM). Feed rate refers to how fast the machine moves laterally through your material, measured in inches per minute (IPM). View Slitting Saw Feeds & Speeds Guide Here
Spindle RPM: Spindle rpm or spindle speed is the rate at which the spindle revolves while cutting. This should also be set to a value appropriate for the tool being used and the material being cut. It is sometimes possible to cut at a faster feed rate by increasing spindle rpm. If you cut at too low of a feed rate or with too high of a spindle rpm, there is risk of overheating the router bit and burning or melting the workpiece.
Thickness: The dimension from side-to-side on the blade.
Tooth Cut: the tooth count on a saw blade refers to the number of teeth present on the blade. It is an important factor to consider when selecting a saw blade because it determines the quality of the cut, the speed at which the cut is made, and the type of material the blade is suitable for. In general, blades with a higher tooth count produce a smoother cut but take longer to make the cut. Conversely, blades with a lower tooth count make the cut faster but may leave a rougher finish.
Tooth Pitch: the distance from the tip of one tooth to the tip of the next tooth.
Tooth Rake Angle: the angle of the tooth face measured with respect to a line perpendicular to the cutting direction of the saw.
TPI: the number of teeth per inch as measured from gullet to gullet.
Width: the nominal dimension of a saw blade as measured from the tip of the tooth to the back of the band.
Precision Saw Arbors - 5025 Series (SAP) (SAP-E Extended Journal)
Our most popular style of slitting saw arbor is available in guaranteed TIR grade SAP (border .0002” TIR) and the extended journal version SAPE. When ULTRA Precision is required the SAP guide is suggested as they are held to stringent quality standards required by discerning Swiss-type machinists.
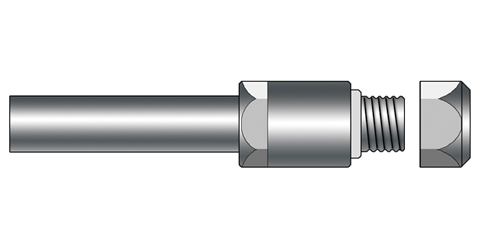

Combination Saw Arbors - 5015 Series
GenSwiss combination arbors are made from pre-hardened material and exemplify what it means to be called “Swiss Precision”. The addition of the combined mill or center drill provides additional tool capacity and setup flexibility.
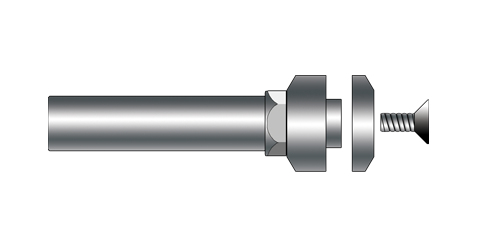
Flange Saw Arbors - 5020 (SAF)
These metric flanged saw arbors provide maximum saw balance and stability with the flange mount design. The unique design applies pressure to the outward edge of the flange ensuring the greatest gripping power at the outer most edge to prevent slipping. Uses countersunk screw and flange washer to apply holding force. Measured TIR is less than .0002”.
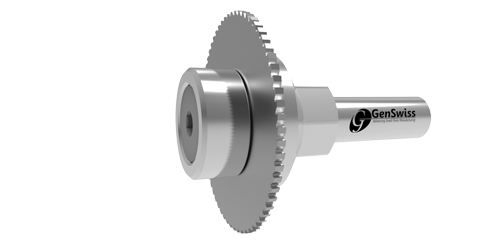
Custom Slitting Saw Arbors
GenSwiss has the capability to assist with the engineering and manufacture of special gang slotting arbors that also feature the option of holding an end mill, spot drill or other small round shank rotary tool.
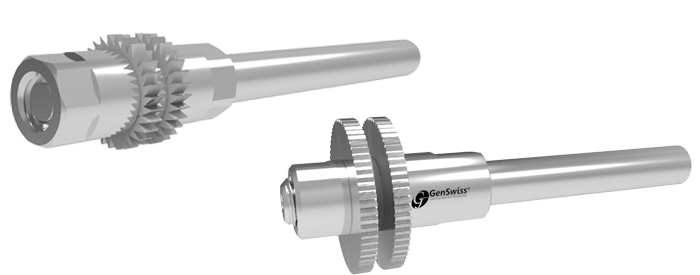
Features we can provide:
• Spacers for gang slotting with multiple blades.
• Custom hub widths (L1 dim.) for oversize blade thickness.
• Optional shank sizes for special applications.
Call 413-562-4800 for more information and order today.
WHAT ARE SLITTING SAW BLADES?
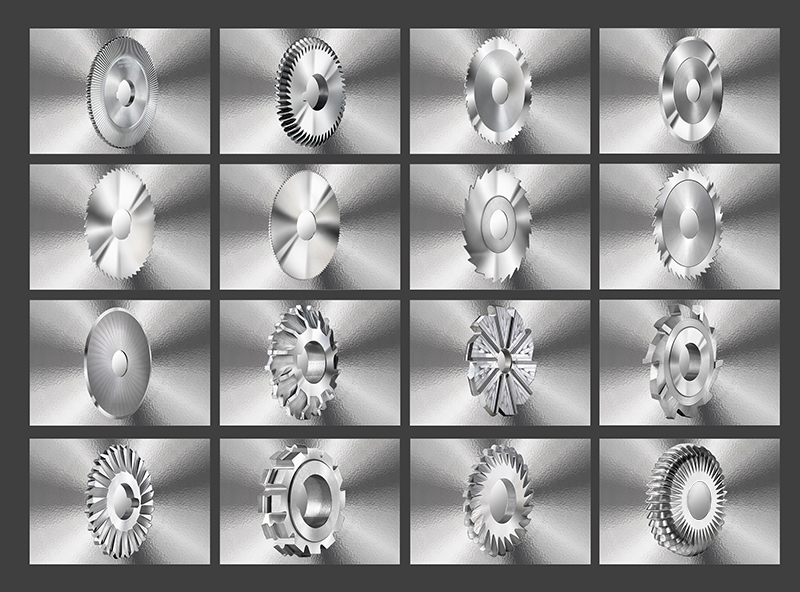
Slitting saws are typically used to cut very narrow through slits or slots in material. Genswiss offers a complete line of saw blades in a wide selection of solid carbide grades with tooth counts ranging from 40-120 teeth per saw. If you are going more than about 4-6x the slot width in depth, an endmill will have rigidity and deflection problems, whereas with a slitting saw the cutting forces are directed more effectively, and the saw will do a faster and better job. They can also be handy for performing certain kinds of undercut operations.
GenSwiss Saw Arbors & Ti-Loc Products are popular choices to mount Slitting Saws. View Ti Loc Product Knowledge page.
WHY USE A SLITTING SAW?
These saws are designed for cutting into both ferrous and non-ferrous materials, and by utilizing their unique shape and geometries, they can cut thin slot type features on parts more efficiently than any other machining tool. Non-Ferrous slitting saws have fewer teeth, allowing for aggressively deep depths of cut.
Capabiliites include milling, drilling, boring, reaming, turning, threading, tapping, knurling, broaching, countersinking, cutting, and facing.
Suitable for industrial and consumer applications that involve cutting metals (tubes, profiles, shafts); blade widths of .0039 inch to .1181 inch or 0.10 mm to 3.00 mm.
ADVANTAGES OF SAW BLADES
- Solid carbide saw blades provide strength and durability
- Can be used for all types of metals
- Works on Ti-Loc Saw Arbors
- Produces more parts in less time
- Can be used on every application
Our saw blades are designed to handle the toughest structural cutting applications.
Saw blades come in various sizes and configurations to fit various saw models and cutting applications. The blade size is often determined by the diameter of the saw blade and the saw arbor sizes.
When selecting a saw blade, it is important to consider the material being cut. Different types of materials require different tooth counts to achieve the best results.
View Speeds and Feeds https://genswiss.com/slitting-saws-support
View Saw Application Selection Guide
 |
GenSwiss Saw Arbors are patented designs of GenSwiss® Signature Series Line of Premium Products made in the USA. Standard and custom orders are available. We strive to deliver products which meet or exceed customer expectations, providing a reliable service with application solutions. Contact us for more information 1-413-562-4800 |











