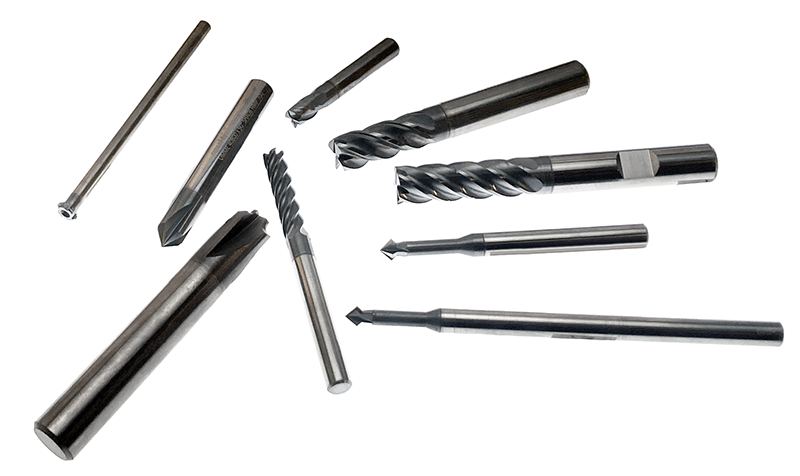
END MILLS
Multidec®-MILL & Multidec®-MICRO TOOLS
GenSwiss® a company of UTIIS® offers two new product lines of end mills and finishing tools for manufacturing.
The first offering is the multidec-MICRO TOOLS U-MILL for micro-machining available in solid carbide 2 and 3 flute end mills from Ø 0.2 to 3.00 mm with center cut; and ball nose end mills from Ø 0.3 to 3.00 mm, 0.75×d and 3×d length with center cut and without tooth pitch. The U-HEXALOBE end mills are available in solid carbide with 3 flutes, from Ø 0.20 to 0.30 mm, usable length of 3.5×d₁ and 5×d; and end mills with 4 flutes, from Ø 0.40 to 1.00 mm, usable length of 3.5×d₁ and 5×d₁ perfectly suited for milling a TORX® form.
The next offering is the multidec-MILL universal end-mills product line which includes Scorpion Mill, Eagle Mill and Wolverine Mill designed to excel in a wide range of materials suitable for general machining as well as long turning with various cutting diameters ranging from 2.00 to-20.00 mm in 3-5 flute geometries, usable length of 2xd, 3xd and 4xd.
(Pictured above are multidec®-MILL solid carbide end mills, deburring tools, front/back deburring tools and concave quarter radius mills)
The right choice of material depends on factors such as the workpiece material, cutting speed, and required surface finish. For more information call us at 413-562-4800. Our skilled GenSwiss staff is dedicated to providing you with the knowledge and assistance you need to find the right combination of tools for your application.
WHAT ARE THE BEST-CASE USES OF END MILLS
End mills are designed to help shops of all sizes maximize tool life and productivity and reduce downtime whether by cutting out large amounts of material or producing fine surface finishes on materials as diverse as hardened steel for mold and die, heat-resistant superalloys for aerospace, titanium and nickel-titanium alloy for medical applications.
When selecting the end mill, you must know what operation you need to perform. The typical operations of the end mill machining may include slotting, roughing, finishing, plunging, profiling, contouring and complex 3D machining tasks. Additionally, end milling can improve the surface finish of workpieces when utilized as a post-process following casting or other less refined cutting techniques. It is precise and accurate, making it suitable for tasks that demand tight tolerances.
End milling is a key process in both prototyping and production environments, allowing you to scale production from trial to moderate and potentially high-volume production.
END MILL GLOSSARY TERMS
Angular Edge: the cutting edge that is a straight line and forms an angle with the cutter axis. The cut that an Angular edge tool produces will not be as flat as a helical cutting edge.
Application: end mills are used in milling applications such as profile milling, tracer milling, face milling, plunging, contouring, slotting.
Carbide: this material resists heat and offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making the compound ideal for high-speed machining and hard materials.
Chamfer End Mills: have a flat tip with angled sides and are designed to create angled surfaces, providing a smooth transition between different surfaces or eliminating sharp edges.
Chip Load: would be the thickness of the provided machined chip. Having a good chip load rate is important as it reduces the heating of the material or tool.
Clearance: space created by the removal of additional tool material from behind the relief angle.
Coated or Non-coated: it's advisable to use the HMP 700 or HMP600 (AlCr-coated) end mills as coatings help increase performance, provide longer tool life with more aggressive running parameters and allow better-quality chip evacuation in comparison to the non-coated.
Convex: an outward projection radius feature on the end face of a ball mill.
Corner Radius End Mills: have a rounded corner on the tip and are used for milling rounded corners.
Cutter Diameter: width of the end mill's cutter.
Cutter Edge: the sharp edge of the end mill tooth, also known as the tooth face or rake face, which removes the material from the workpiece.
Depth of Cut: depending on how deep you want your end mill to go inside the material, you will have to adapt your feed rate to spare it.
End Gash: the process of removing material from an end mill to create web thickness along the very top of the tool.
End Teeth: the sharp cutting edges at the top of the end mill, also known as axial teeth.
Flat end Mill: named for the flat tip of its cutter, these tools are used for roughing operations, cutting 2D shapes, and flat-sided 3D shapes. Also known as straight or square end mills.
Feed Rate & Speed: the speed of the end mill cutting tool being used over the material would be the Feed Rate. At the same time, the rate of rotation of the bits will be termed Speed. The rate of spindle turning endmills determines the speed. Both these aspects will change depending upon the material of use.
Flutes: provide the end mills power to cut through rough and hard surfaces, flutes are the grooves present on the bits. The more the flutes, the higher the tool strength while fewer flutes will have higher chip space.
-
Double Flute/Two Flute - provides a higher flute volume but they deliver slower feed rates. They allow for more chip carrying capacity and are used primarily in slotting and pocketing nonferrous materials. They can also be used for grooving, and sometimes used for plunge milling.
-
Triple Flute/Three Flute - Have the same flute space as two flutes, but also have a larger cross-section for greater strength. They are used for pocketing and slotting ferrous and nonferrous materials. Known for delivering lesser vibrations during cutting and engraving tasks.
-
Four Flute/ Quad Flute - Allow for faster feed rates, but due to the reduced flute space, chip removal may be a problem. They produce a much finer finish than two and three flute tools. Ideal for peripheral and finish milling. You can also use these for pocketing and slotting tasks.
-
Five Flute/ - Have smaller flute spacing than four-flute end mills, allowing for more strength. Better suited for high efficiency milling and hard materials.
Flute Washout: the amount of non-cutting flute area that extends past the cutting edges.
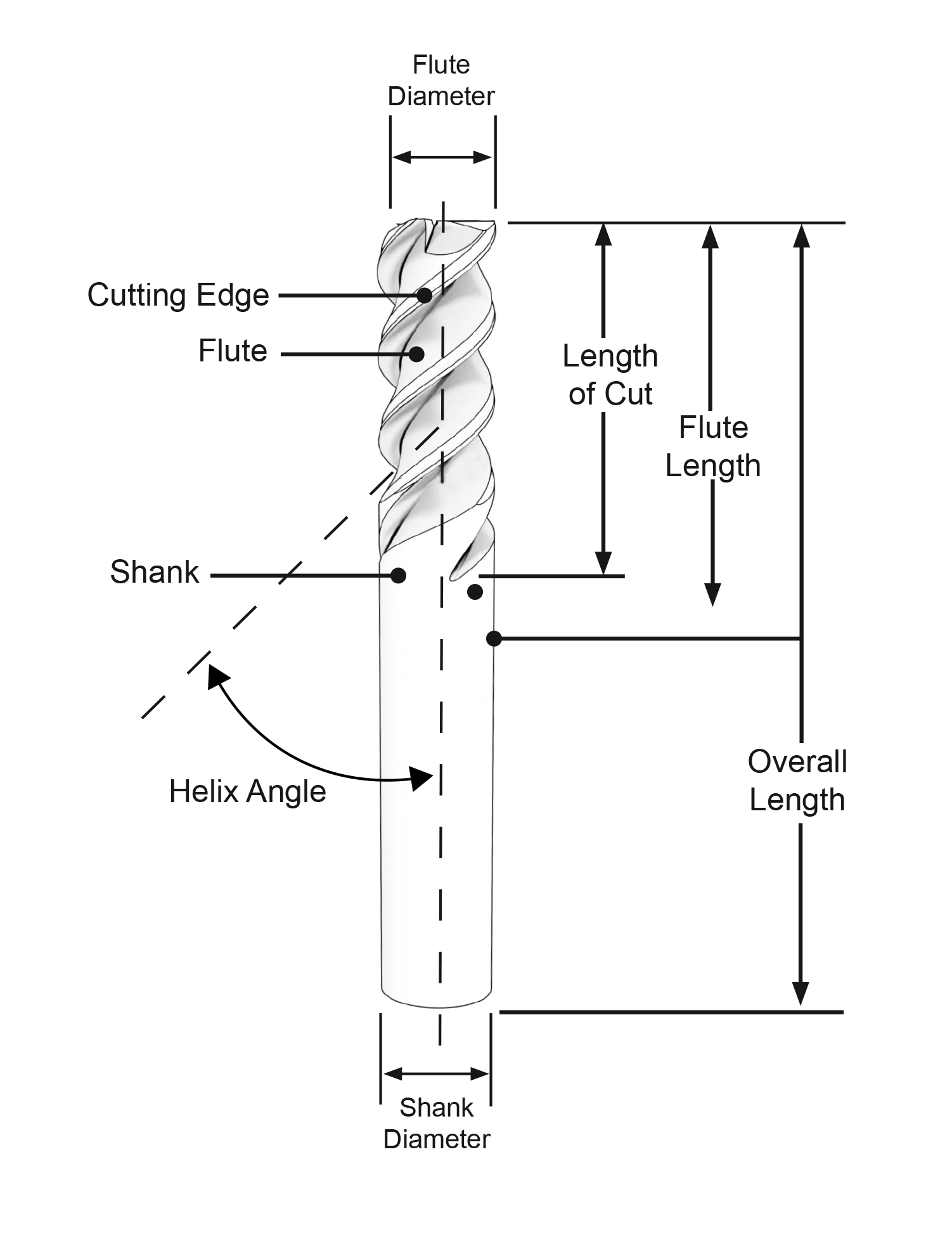
Helix Angle: the angle measured from the centerline of the tool and a straight-line tangent along the cutting edge.
Length of Cut/Flute Length: the functional cutting depth with the tool in the axial orientation.
Machine Operations: Common machining operations include roughing, slotting, finishing, contouring, plunging and high efficiency milling.
Overall Length (OAL): Measurement from end to end.
Pitch: the degree of radial separation between the cutting edges at a given point along the length of cut, most visible on the end of the end mill.
Plunge Mill: dig deep vertically into the surface.
Profile: end mills can have different profiles, such as square, corner radius, or ball.
Roughing End Mills: have a serrated or scalloped edge and are used for removing large amounts of material quickly. They are great for roughing out parts and for creating a rough finish on a part.
Shank Diameter: the width of the shank – the non-cutting end of the tool that is held by the tool holder. This measurement is important to note when choosing a tool to ensure that the shank is the correct size for the holder being used. Shank diameters require tight tolerances and concentricity in order to fit properly into any holder.
Shank Flat: a flat area ground on the shank used with a set screw to prevent pull out in certain types of holders. This could be referred to a Weldon flat, long flat, or tapered flat.
Side Teeth: the cutting edge on the side of the tool, also known as radial teeth.
Square End Mills: are the most common ones and can be used for many milling applications, including slotting, profiling and plunge cutting. They are great for creating square bottomed slots and pockets, and for cutting flat surfaces.
Straight Shank: a cylindrical shank, with or without driving flats or notches, often seen on Carbide end mills.
Tapered End Mills: have a tapered tip and are used for creating tapered holes or channels. They are great for creating parts with a conical shape.
Tooth: the cutting edge of the End mill, also known as the rake face. The portion of the tooth upon which the tooth meets the part.
TORX®: is a star-shaped wave profile with six rounded lobes. Compared to classic screw profiles, TORX® can be used to transfer a higher torque without damaging the bit and screw.
THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF END MILLS
Listed below are the different types of end mills:
Roughing End Mills
A roughing end mill also known as hog mills, are used to efficiently remove large amounts of material from a workpiece, especially during the initial stages of machining. It is designed with a coarse and rugged geometry that allows for aggressive material removal while withstanding high cutting forces. Roughing end mills remove heavy material while providing a smooth finish in a single pass. Great for roughing out parts and for creating a rough finish on a part.
Ball End Mills
A ball end mill also known as ball nose end mill, are designed to provide precision contouring, slotting, and machining of complex 3D shapes. The spherical tip allows for smooth and accurate machining of concave surfaces, filets, and curved profiles, smoothing the cuts into each other with minimal aliasing. Ball end mills can be used for both roughing and finishing operations — as well as in 3D contouring applications — simply by varying cut depth and feed rate. They generate lower cutting forces than flat end mills, as the cut transitions into the material progressively along the bit’s radius.
Concave Quarter Radius End Mills

A concave quarter radius end mill also known as a corner rounding end mill, is a specialized cutting tool used to round the sharp internal corners of a workpiece. They are used for creating tool-defined filets on internal (and to a lesser extent external) corners of cuts. Rounding sharp corners removes sources of stress concentrations in parts. These tools are ideal for contouring and finishing work and blending surfaces between different features.
Front/back Concave Quarter Radius End Mills

A specialized milling cutter designed to create concave (inwardly curved) profiles on a workpiece, it has a rounded, inward curve on both the front and back faces of the cutting tool, allowing for smooth, seamless concave cuts on the material being machined. These tools are used to mill rounded edges or grooves with a consistent curvature on both sides of the cut.
Trochoidal End Mills

To optimize performance, Trochoidal end mills often have a high flute count to facilitate chip removal and achieve a better surface finish. Designed specifically for use in trochoidal milling, a machining technique that employs a continuous spiral tool path with a low radial depth of cut and high axial depth of cut, resulting in reduced cutting forces, improved chip evacuation, and extended tool life, particularly when machining deep slots or pockets in hard materials. It can be considered a versatile tool capable of both roughing and finishing depending on the machining parameters used.
Center Cut End Mill

Center cut end mill is a milling tool with cutting blades both on the face and on the side of the end mill. Therefore, it can plunge directly into the workpiece using its face blades, and also move inside the workpiece by cutting with its side blades. Ideal for Plunge Cutting, Slotting, Profile Milling, Face Milling, Ramp Milling.
End Mill for Milling TORX® Contour

End mill for machining of TORX® contour in titanium and stainless-steel screws for medical technology. Maximum geometric and concentric precision make these tools ideal for reliable milling in large scale volume production.
Weldon Flat

Weldon Shank end mills are produced with a Weldon flat on the cutter to provide a positive (non-slip) driving surface to the end mill.
If you are interested in learning more about end mills and how they can be used in the manufacturing process, GenSwiss is a great resource. Our team of experts will help provide guidance and advice on the best tools and techniques for your specific needs. To learn more, visit the Contact Us page or call 413-562-4800 or email [email protected] . Whether you are a small business owner or a large manufacturer, GenSwiss can help you achieve your production goals wiht high-quality end mills and other manufacturing services.









